원자력 안전 및 에너지 변환 분야 | Siphon breaking
페이지 정보
2017.02.07 / 2,005관련링크
본문
Research
reactors are nuclear reactors which were developed for neutron based research
industry rather than for power generation. Water in the reactor pool acts as
the moderator, reflector, and shielding barrier to radioactivity from the
nuclear reactor fuel rods. Moreover, the coolant in the reactor pool provides
the ultimate heat sink during accidents in which the pump of primary cooling
system stops working. The quantity of coolant is strongly related to the length
of time for which safety can be maintained between the onset of coolant loss
and exposure of the fuel rods after the occurrence of such accidents. For these
reasons, the water level in the reactor pool must be maintained higher than the
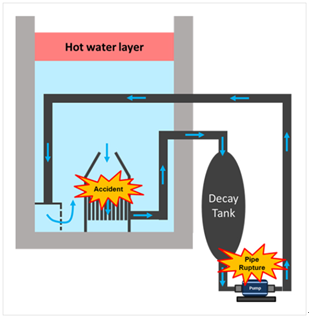
minimum safe level. If the pipe ruptures, the siphon phenomenon causes
continuous loss of coolant from the reactor pool until the phenomenon is stopped.
In extreme cases, the nuclear fuel rods in a reactor pool would be exposed to
ambient air. (Fig. 1) To avoid this type of accident, use of a siphon breaker
has been suggested as a nuclear safety device for research reactors.